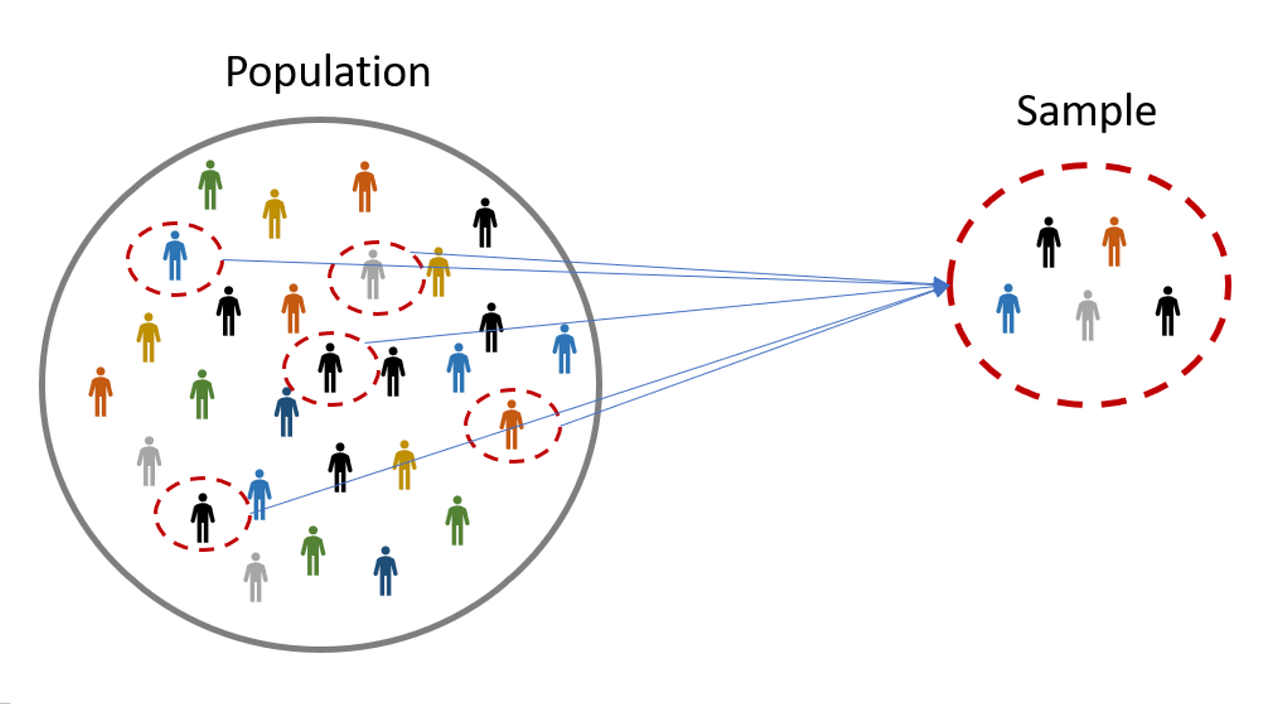
Sampling Vs Measurement Bias . Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. Sampling bias occurs when a sample does not represent the population, skewing the results of studies and experiments. Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they.
from medium.com
Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they. Sampling bias occurs when a sample does not represent the population, skewing the results of studies and experiments. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical.
Population, Sample, Parameter, Statistic, Biased, Unbiased ngbala6
Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias occurs when a sample does not represent the population, skewing the results of studies and experiments. Sampling bias occurs when a sample does not represent the population, skewing the results of studies and experiments. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they. Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values.
From medium.com
Population, Sample, Parameter, Statistic, Biased, Unbiased ngbala6 Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias occurs when a sample does not represent the population, skewing the results of studies and experiments. Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Measurement bias occurs when information collected. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.questionpro.com
Sampling Bias Types, Examples & How to Avoid It QuestionPro Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Measurement bias occurs. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From kyloot.com
5 Most Common Sampling Errors (2022) Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. Measurement. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From bookdown.org
5 Measurement and Sampling (9/7) MUED 540 Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. Measurement. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From forms.app
What is sampling bias types & examples forms.app Sampling Vs Measurement Bias When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population.. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Sampling Bias PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2771567 Sampling Vs Measurement Bias The incorrectly measured variable can be either. When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. Because there is. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT 4.4 Statistical Bias PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Sampling Vs Measurement Bias When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.youtube.com
Sample statistic bias worked example Sampling distributions AP Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.researchgate.net
Attribute sampling biases in valuation. The valuation of a good may be Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias occurs when a sample does not represent the population, skewing the results of studies and experiments. When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. Measurement bias. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.questionpro.com
Research bias What it is, Types & Examples QuestionPro Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn.. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.investopedia.com
Sampling Errors in Statistics Definition, Types, and Calculation Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. Sampling bias occurs when a sample does not represent the population, skewing the results of studies and experiments. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. When this bias occurs,. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Sampling PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6747258 Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. When there is sampling bias in. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From limbd.org
Types of Sampling Design Library & Information Management Sampling Vs Measurement Bias When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they. Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Measurement bias or information bias refers. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Sample Bias Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they. Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Mastering Strategic Management Chapter 10.3 to End Decision Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. Hence, sampling bias produces a distorted view of the population. Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From medium.com
What is the Sampling Bias?. Drawing a valid conclusion depends… by Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of key study variables. The incorrectly measured variable can be either. Bias occurs if the study population does not closely represent a target population. Sampling bias can significantly. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From fity.club
Sampling Bias Sampling Vs Measurement Bias Sampling bias can significantly affect statistical. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). Measurement bias occurs when information collected for use as a study variable is inaccurate. Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which it was drawn. Measurement bias or information bias refers to the distorted measurement of. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.
From statisticseasily.com
Sampling Bias A Comprehensive Guide Sampling Vs Measurement Bias When this bias occurs, sample attributes are systematically different from the actual population values. When there is sampling bias in your study, differences between the samples from a population and the entire population they. Because there is a systematic (i.e., nonrandom). Sampling bias in statistics occurs when a sample does not accurately represent the characteristics of the population from which. Sampling Vs Measurement Bias.